 |
 |
- Search
|
|
||
Abstract
Ossification of the posterior longitudinal ligament (OPLL) in the cervical spine and related neurological complications are not uncommon in East Asian countries. The estimated prevalence of cervical OPLL-related hospitalization is 7.7 per 100,000 person-years in Taiwan, and higher incidence rates have been observed in elderly and male patients. Although cervical OPLL is frequently insidious, it can eventually cause myelopathy and predispose patients to spinal cord injury (SCI). There are multiple options for managing cervical OPLL, ranging from observation to many kinds of surgical procedures, including posterior laminoplasty, laminectomy with or without fusion, anterior corpectomy with or without instrumentation, and circumferential decompression and fusion. None of these surgical approaches is free of complications. However, to date, there is still a lack of consensus regarding the choice of the surgical approach and the timing of surgical intervention. Cervical SCI and related neurological disabilities are more likely to occur in OPLL patients, who should therefore be cautioned regarding the possibility of a subsequent SCI if treated without surgery. This article aimed to review the prevalence, management strategies, and prognosis of cervical OPLL.
Ossification of posterior longitudinal ligament (OPLL) in the cervical spine and related neurological complications are not uncommon in countries of Eastern Asia, including Korea, Japan and Taiwan. In contrast, in among Caucasian population, cervical OPLL is a rare disease that, nevertheless, can cause cervical radiculopathy and myelopathy of varying severity [1]. Literature from Japan had the earliest description of the disease, as well as much discussion regarding the management of cervical OPLL with posterior laminoplasty. However, due to the rarity of the disease per se and various severities of neurological function upon presentation, the natural disease course of cervical OPLL remains elusive [2]. Therefore, it remains controversial among experts as to whether surgery is necessary, what is the optimal timing of intervention, and how should the surgical approach reach maximal safety.
The classic debates of surgical approaches to cervical OPLL have been between the advocates of anterior versus posterior approaches [2-5]. The anterior approaches, including single and multiple levels of corpectomy, oblique corpectomies, or floating of the egg-shelled OPLL, were usually more technically demanding. Since these anterior approaches could directly decompress the spinal cord, one would often expect more neurological improvement than observation or posterior approaches [5]. However, these challenging surgeries were not without complications and morbidities. For examples, dysphagia, hoarseness, cerebrospinal fluid leakage and subsequent pseudomeningocele, excessive epidural hemorrhage, spinal cord injury (SCI) and neurological deterioration were not uncommon in the anterior approaches [6-15]. In contrast, the posterior approaches were easier, safer, and could cover multiple segments at once. Typically, multilevel posterior laminoplasty or laminectomy could be carried out for long-segment cervical OPLL with low rates of surgical complications [5,16]. There were modifications of posterior laminoplasty, including French- and single-door, with and without implants. Moreover, there were also surgeons who performed laminectomies with lateral mass or pedicle screw fixation in these OPLL patients. There were pros and cons for all these surgical approaches in the management of cervical OPLL. Each of the approaches had its own limitations and could sometimes be staged or combined.
The aim of this report was to review the authors’ studies in the past decade, focusing on the updated information of cervical OPLL. Epidemiology studies of OPLL in Taiwan and experiences of new surgical modalities, including the technology of cervical disc arthroplasty, were summarized to reflect the current management of OPLL in Eastern Asia.
Although OPLL is apparently more common in countries like Korea, Japan, and Taiwan than the Western countries, it is still far less frequently encountered than other degenerative spinal disorders. Also, along the entire spine, the cervical region was the most common site of development of OPLL [1]. However, estimation of the incidences of cervical OPLL remained difficult and was not adequately reported in the literature, because cervical OPLL had various presentations. Many of the cervical OPLL would not become symptomatic until it became massive and caused severe spinal cord compression. Owing to the advancement of technology in neuroradiology, the degree and extent of cervical OPLL can be depicted by computed tomography (CT) and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) at an earlier stage than decades before. Nonetheless, estimation of the incidences of cervical OPLL would largely depend on the definition of OPLL (e.g., symptomatic or asymptomatic).
The largest cohort of OPLL so far was reported by Wu et al. [1] in 2011. The study included a series of patients with cervical OPLL during a span of a decade for investigation of the incidence, prevalence, hospitalization, and surgical treatment. In the large cohort of this Taiwanese or Chinese population, the incidence of cervical OPLL-related hospitalization was 6.1 per 1,000,000 person-years, and its prevalence rate was 7.7 per 100,000 person-years. Higher incidences were observed in elderly and male patients, which imply the degenerative nature of the disease. After adjustment for demographics, the incidences and trends of OPLL-related comorbid disability were associated with age and surgical approaches. The study utilized the National Health Insurance Research Database (NHIRD), provided by the National Health Research Institutes of Taiwan, which is a national database containing the records of over 25 million people of Taiwan. The national health insurance of Taiwan, run by the government, features an extremely high coverage (over 99% of the population), and yields an unique system that finances healthcare for the entire population and offers unrestricted access to any healthcare provider of the patients’ choice. Therefore, the statistics gathered represented a sound epidemiologic investigation of incidences of diseases and utilization of medical interventions because of universal coverage.
All other previously reported prevalence rates, varying from 0.1% to 4.6% in different ethnic groups including Caucasians and Japanese, were largely calculated from institutional radiographic databases. These radiographic prevalence rates might be influenced by the population included for sampling, and should not be considered representative of the endemic reality. The data from all patients, whether or not symptomatic, who underwent imaging studies of the cervical spine for various reasons in certain institutions, inherently had selection bias. The selection bias from institution-based data becomes more prominent considering the rarity of the disease [1].
Cervical spondylotic myelopathy (CSM) causes spinal cord dysfunction of various degrees and can be associated with multiple pathologies, including herniated intervertebral discs, hypertrophy of ligamentum flavum, and OPLL [17]. The optimal timing and strategies for management of CSM remain uncertain and debatable in neurosurgical practice [18]. Since spondylosis and stenosis that cause neurological dysfunctions might not be reversible, some surgeons would suggest early surgery for patients with CSM to ameliorate the risk of SCI [17,19-25]. To date, there are insufficient data to correlate CSM with SCI, and whether or not the risk of SCI can be altered by surgical intervention remains elusive. Furthermore, surgical treatment for OPLL that causes severe CSM is challenging because resection of OPLL is often difficult and might be associated with serious complications. Strategies to manage CSM with OPLL are thus diversified and the timing of intervention is quite debatable, especially when the symptoms are mild.
Wu et al. [17] conducted a study in Taiwan, which included 14,140 CSM patients, to analyze the incidences of CSM as well as the subsequent risks of SCI. They used the NHIRD, the comprehensive nationwide cohort, with a total observation period of more than 12 years. During the follow-up, CSM caused hospitalization at a rate of approximately 4 per 100,000 person-years. As expected, higher incidences of the relatively severe CSM that required hospitalization were found in the elderly and male population. Furthermore, the subsequent incidences of SCI in these patients with CSM were as high as 12.33 per 1,000 person-years, and cervical SCI was approximately 1.5 times more likely to happen among CSM patients who were managed without surgery than those who had surgery. They concluded that patients with CSM treated conservatively should be cautioned for subsequent SCI. The report, which was the first study focused on the epidemiology of CSM on a national scale, highlighted the importance of surgical intervention in patients of SCM. Moreover, as previously reported, CSM was more commonly seen in older male patients [26]. This was similar to previous reports that demonstrated higher incidences of cervical OPLL, as a known cause of CSM, observed among elderly and male patients [1]. These results implied the degenerative nature of both CSM and cervical OPLL.
Chen et al. [4] published a study using the national database of Taiwan to evaluate patients with CSM and OPLL and subsequent risks of SCI. The study aimed to analyze the incidences of subsequent SCI in patients with CSM. The differences in risk of SCI were compared between patients with CSM not only with and without OPLL, but also with and without surgery, respectively. The overall incidence of SCI in these CSM patients was 2.0 per 1,000 person-years. Patients who had CSM with OPLL and were conservatively managed had the highest incidence of SCI at 4.1 per 1,000 person-years. Patients who had CSM with OPLL and were surgically managed had a lower incidence of SCI at 3.7 per 1,000 person-years. Patients who had CSM without OPLL and were conservatively managed had an even lower incidence of SCI at 2.4 per 1,000 person-years. Patients who had CSM without OPLL and who were surgically managed had the lowest incidence of SCI at 1.3 per 1,000 person-years. The paper demonstrated that SCIs were significantly more likely to happen in patients of male gender and with OPLL. Surgery could significantly lower the risk for approximately 50%. The report then concluded that patients with CSM had an overall incidence rate of SCI at approximately 0.2% per year. The male gender, coexistence of OPLL, and conservative management were twice as likely to cause subsequent SCI. Surgery was therefore suggested for male CSM patients who also had cervical OPLL.
There was little controversy on surgical treatment for patients with severe CSM caused by OPLL, despite that various surgical approaches that had been proposed effective in improving neurologic functions [27-31]. To rescue neurological dysfunctions, these surgeries were deemed necessary, though some of the operations could cause complications. The most commonly debated issue among neurosurgeons was whether surgery should be indicated when the OPLL caused minor symptoms or mild CSM. Usually the OPLL in the cervical spine developed gradually and remained insidious until it caused significant spinal stenosis and when the myeloradiculopathy became bothersome. When the OPLL became symptomatic, the pressure exerted onto the spinal cord by the pathologically calcified ligament and subsequent neurological dysfunction might be rapidly progressive and irreversible [32-34]. However, it is not uncommon for OPLL patients with spinal stenosis to remain myelopathy-free for a long period of time [35,36]. Thus, there were reports advocating no surgery for asymptomatic or mildly symptomatic patients despite markedly evident cervical OPLL as demonstrated by CT or MRI with radiographic evidence of myelopathy [35,37]. In contrast, there were studies associating SCI to the presence of OPLL [38-40] and some authors advocated early surgery for better neurologic recovery [41,42]. In summary, the optimal timing of surgical intervention for intact spinal cord function or mild myelopathy caused by cervical OPLL has remained controversial in the past decade. Whether the chance of SCI was increased if asymptomatic or mildly symptomatic OPLL was managed conservatively has been inferred but never elucidated in a controlled study.
Cervical SCI and related disabilities are more likely to happen in OPLL patients, who should be cautioned for subsequent SCI if treated conservatively [2]. Wu et al. [2] published another study to address such an issue of OPLL management and risks of subsequent SCI. The study used a comprehensive national database to investigate the incidence of SCI in 265 patients who had cervical OPLL that was managed without surgery. These conservatively managed cervical OPLL patients were compared to 5,339 of age- and sex-matched controls after adjustment for comorbidities that may predispose to SCI, including osteoarthrosis, osteoporosis, rheumatoid arthritis, and scoliosis. When compared to those matched non-OPLL controls, these nonsurgically managed OPLL patients had significantly higher rates of subsequent SCI. The adjusted hazard ratios were 32.2 for hospitalized SCI and 104.8 for disabled SCI. The remarkable disparity in the risk of subsequent SCI can be valuable in choosing management strategies for OPLL patients.
The surgical strategies for cervical OPLL, including the anterior-only approach, posterior-only, or combined anterior-and-posterior, has been a classic topic for debate in neurosurgery. Each of the approaches has its advantages as well as disadvantages and should be tailored to each individualized condition. In this article, we aimed to summarize the authors’ experiences with several published papers that addressed patients with cervical OPLL.
Most of the complications, such as transient hoarseness and dysphagia, of the anterior cervical approach were self-limiting and patients usually recovered after a few days or weeks. Although frequently recovered spontaneously after months, temporary C5 paresis or palsy involving the deltoid and/or biceps brachii muscles could cause a lot more disappointment for the patients. This could occur following either anterior or posterior cervical spinal surgery, in patients with and without OPLL. The actual etiology, risk factors, and prognostic factors for the temporary C5 palsy remain uncertain to date. The incidence was frequently reported in a series of cervical decompression surgery to range from 0%–17% [43-45]. Both anterior cervical corpectomy and fusion (ACCF) and laminoplasty are accepted procedures to treat cervical stenosis and OPLL [5,46-49]. In the literature, there were more reports of C5 palsy with posterior cervical decompression surgery than with anterior cervical surgery [44,50-63], though both anterior cervical discectomy and fusion and ACCF could also be associated with postoperative C5 palsy [43-45,64,65]. Despite the knowledge that a C5 palsy is a risk of either procedure, the relative risk of C5 palsy with anterior versus posterior surgery remains uncertain, especially when OPLL is involved.
Mummaneni and colleagues [17,36] conducted a retrospective review of 31 ACCF (at C4 or C5) and 31 instrumented laminoplasty cases performed to treat CSM, including those with and without OPLL [5,16]. The demographics of the 2 groups were similar except that the ACCF group was younger by approximately 9 years. The mean number of levels treated was higher in the laminoplasty cohort compared to the ACCF cohort. During the mean clinical follow-up of 14 months, there was no statistical difference between the complication or reoperation rates between the 2 groups. There were a total four C5 nerve root paresis (2 in each group), and 3 patients recovered deltoid function within 18 months. The authors concluded that both the ACCF and laminoplasty were effective treatments for patients with CSM, and there were no differences in the rate of deltoid paresis between ACCF and laminoplasty to treat cervical stenosis. However, the severe deltoid paresis patients required a longer time to recover than did the mild ones.
The study published by Mayer et al. [5] demonstrated that laminoplasty was an effective treatment for CSM caused by either degenerative spondylosis or OPLL. In the study, laminoplasty patients with segmental OPLL had similar perioperative parameters to patients with degenerative spondylosis but not OPLL. Perioperative complications and reoperations were fewer in the OPLL group, although the degenerative spondylosis patients had better neurological outcomes than the OPLL group. Patients with degenerative spondylosis or segmental OPLL maintained most of their baseline dynamic cervical spine motion after laminoplasty. Thus, laminoplasty seemed to be an effective strategy for preservation of segmental motion in patients with CSM caused by OPLL. Since degenerative stenosis and OPLL were 2 common causes of CSM, the study postulated that patients with OPLL have more complications and worse outcomes than those with degenerative stenosis. The study also compared the outcomes of 40 instrumented laminoplasty for CSM patients due either to degenerative changes or to OPLL. Over 4 years, 12 patients with degenerative cervical stenotic myelopathy were compared to the remaining 28 patients with segmental OPLL. The degenerative stenosis group had a better mean preoperative Nurick score than the OPLL group. Postoperatively, the degenerative group had more complications but a greater improvement in Nurick scores compared with the OPLL group. The other parameters (blood loss, length of stay, VAS neck pain scores, and range of motion) were similar for both groups. Therefore, the authors concluded that laminoplasty appears to be an effective method of treatment for cervical stenosis due to either degenerative changes or OPLL. Although this was a series of a relatively small number of patients, the demonstrated results were compatible with many other reports that advocated posterior decompression for cervical OPLL.
Anterior cervical approaches, including corpectomies and discectomy, were also valid strategies in the management of cervical OPLL [3]. For short segment OPLL with multilevel CSM, the construct of hybrid cervical disc arthroplasty (CDA) and ACCF seemed to be a reasonable option as it not only allowed preservation of segmental mobility but also provided thorough decompression of the OPLL. For instance, Chang et al. [3] published a series about CSM patients who had multilevel (≥ 3 levels) CSM that consisted of dual pathology (segmental OPLL and spondylosis or herniated discs) in the subaxial cervical spine. A hybrid surgical strategy ACCF for segmental OPLL and CDA for disc herniation or spondylosis was applied. Even though the number of patients included in the current study was relatively small (n=15), these patients all did very well during the follow-up of approximately 18 months. The standard clinical outcomes (VAS, NDI, JOA, and Nurick scores) all had significant improvement. The hybrid construct also worked out well with intended function, as all the ACCF achieved arthrodesis, while all the CDA demonstrated dynamic motion on lateral radiographs after 1 year. Thus, the study demonstrated that multilevel CSM caused by segmental OPLL and spondylosis could be managed successfully by hybrid surgery of ACCF and CDA. The clinical and radiological outcomes were satisfactory. Furthermore, although located next to each other, the instrumented ACCF construct and CDA still achieved solid arthrodesis and preserved mobility, respectively. Therefore, hybrid surgery may be a reasonable option for the management of CSM with OPLL.
For continuous-type OPLL in the cervical spine, the authors recommended circumferential decompression and fusion, including laminectomies and corpectomies. By posterior multilevel laminectomy, the dural sac could achieve substantial decompression and shift backward. This maneuver could also create more space for anterior decompression, for example ACCF, and thus made the anterior approach safer. Furthermore, the multilevel posterior decompression could save the need for extensive anterior decompression. In addition, the instrumented laminectomy (with lateral mass or pedicle screw instrumentation from the posterior) could provide remarkable strength of stability, when combined with anterior cervical plates and screws. For such a strategy of a combination of long segments of posterior laminectomy and fusion with anterior corpectomies or discectomies and fusion, less extensive anterior resection of long continuous type of OPLL yielded acceptable outcomes in our institute.
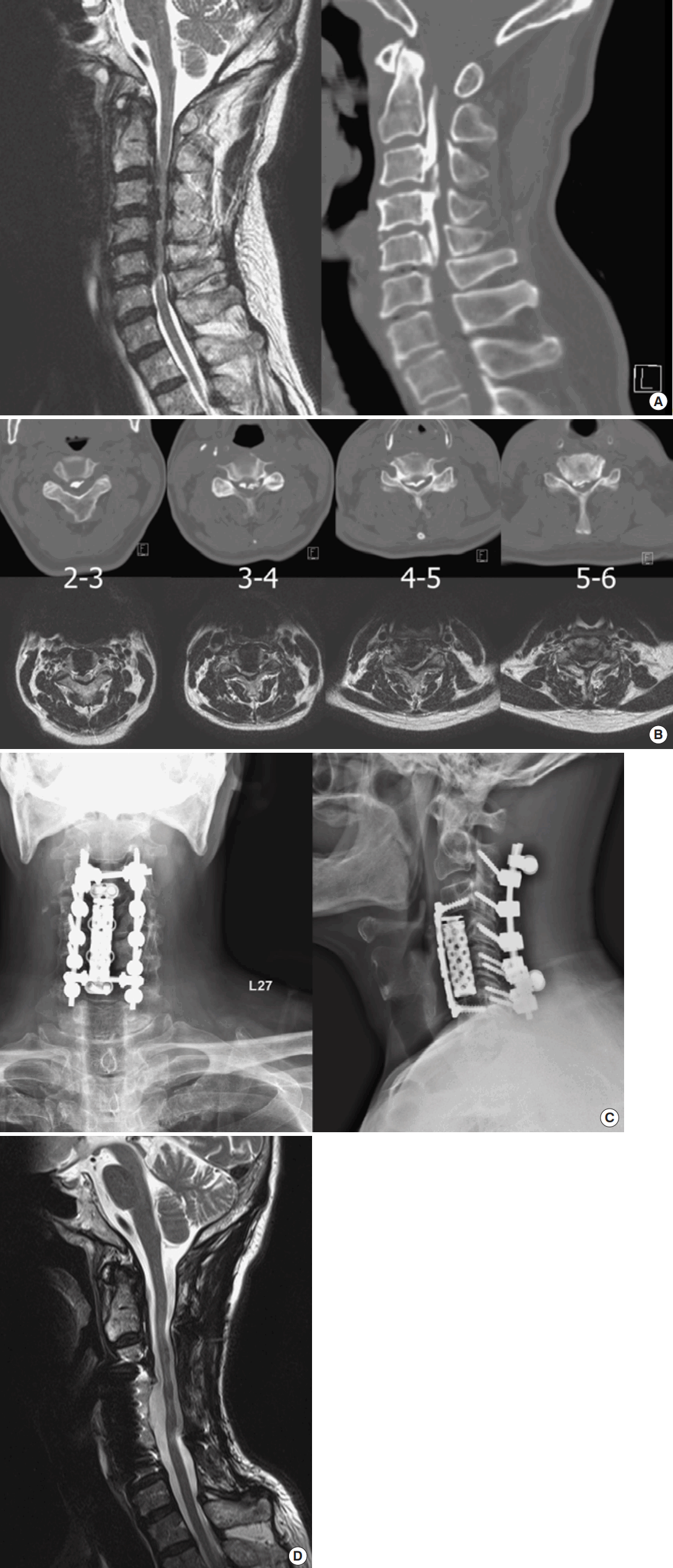
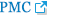
For example, a 61-year-old male patient presented with progressive deteriorating neurological function, which included clumsiness with his hands, lower limb weakness, and claudication for 4 months. His MRI demonstrated multilevel stenosis, and the CT clearly depicted the extensive continuous OPLL from C2 down to C6. (Fig. 1A, B) The patient was consented and taken to the operating room for circumferential decompression and fixation (Fig. 1C). The patient’s hand dexterity improved significantly after the surgery, and his lower limb muscle powers got almost complete recovery. The MR taken postoperative 1 year also demonstrated fully decompression of the OPLL at C3–6 (Fig. 1D).
Cervical OPLL has a higher prevalence rate in East Asian countries than in the Western world. Typically, the higher incidences were observed in the elderly and male patients. Symptomatic patients with OPLL, and those who have CSM, should be cautioned if managed without surgical decompression, because the OPLL and CSM could deteriorate and the myelopathy might not always be reversible, and may predispose SCI. Surgical options for OPLL included ACCF for short and segmental OPLL, laminoplasty for long continuous cases and with kyphotic deformity, and combined in severe long continuous cases of OPLL. However, the best timing of intervention, and the optimal surgical strategy for the patients who have only minor symptoms remains controversial. Longer term follow-up and investigations of the natural history of OPLL are thus needed.
Fig. 1.
Circumferential decompression with instrumented fusion for cervical OPLL. (A) Preoperative sagittal images of T2-weighted magnetic resonance images (MRIs) and computed tomography (CT) demonstrated severe ossification of the posterior longitudinal ligament (OPLL) from C2 down to C5. (B) Axial images of MRIs and CTs at each disc level demonstrated severe cervical stenosis caused by the OPLL. (C) Postoperative radiographs of anterior and posterior decompression and fusion with instruments. (D) Postoperative T2-weighted sagittal MRI taken at 12 months after surgery demonstrated adequate decompression at anterior and posterior aspects.
REFERENCES
1. Wu JC, Liu L, Chen YC, et al. Ossification of the posterior longitudinal ligament in the cervical spine: an 11-year comprehensive national epidemiology study. Neurosurg Focus 2011 30:E5.

2. Wu JC, Chen YC, Liu L, et al. Conservatively treated ossification of the posterior longitudinal ligament increases the risk of spinal cord injury: a nationwide cohort study. J Neurotrauma 2012 29:462-8.


3. Chang HC, Tu TH, Chang HK, et al. Hybrid corpectomy and disc arthroplasty for cervical spondylotic myelopathy caused by ossification of posterior longitudinal ligament and disc herniation. World Neurosurg 2016 95:22-30.


4. Chen LF, Tu TH, Chen YC, et al. Risk of spinal cord injury in patients with cervical spondylotic myelopathy and ossification of posterior longitudinal ligament: a national cohort study. Neurosurg Focus 2016 40:E4.

5. Meyer SA, Wu JC, Mummaneni PV. Laminoplasty outcomes: is there a difference between patients with degenerative stenosis and those with ossification of the posterior longitudinal ligament? Neurosurg Focus 2011 30:E9.

6. Chang HK, Huang WC, Wu JC, et al. Should cervical disc arthroplasty be done on patients with increased intramedullary signal intensity on magnetic resonance imaging? World Neurosurg 2016 89:489-96.


7. Chang HK, Huang WC, Wu JC, et al. Cervical arthroplasty for traumatic disc herniation: an age- and sex-matched comparison with anterior cervical discectomy and fusion. BMC Musculoskelet Disord 2015 16:228.


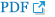
8. Chang PY, Chang HK, Wu JC, et al. Is cervical disc arthroplasty good for congenital cervical stenosis? J Neurosurg Spine 2017 26:577-85.


9. Fay LY, Huang WC, Tsai TY, et al. Differences between arthroplasty and anterior cervical fusion in two-level cervical degenerative disc disease. Eur Spine J 2014 23:627-34.


10. Fay LY, Huang WC, Wu JC, et al. Arthroplasty for cervical spondylotic myelopathy: similar results to patients with only radiculopathy at 3 years' follow-up. J Neurosurg Spine 2014 21:400-10.


11. Mummaneni PV, Amin BY, Wu JC, et al. Cervical artificial disc replacement versus fusion in the cervical spine: a systematic review comparing long-term follow-up results from two FDA trials. Evid Based Spine Care J 2012 3(S1):59-66.



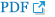
12. Tu TH, Chang CC, Wu JC, et al. Resection of uncovertebral joints and posterior longitudinal ligament for cervical disc arthroplasty. Neurosurg Focus 2017 42(VideoSuppl1):V2.

13. Tu TH, Wu JC, Cheng H, et al. Hybrid cervical disc arthroplasty. Neurosurg Focus 2017 42(VideoSuppl1):V5.


14. Wu JC, Huang WC, Tsai HW, et al. Differences between 1- and 2-level cervical arthroplasty: more heterotopic ossification in 2-level disc replacement: clinical article. J Neurosurg Spine 2012 16:594-600.


15. Wu JC, Huang WC, Tu TH, et al. Differences between softdisc herniation and spondylosis in cervical arthroplasty: CT-documented heterotopic ossification with minimum 2 years of follow-up. J Neurosurg Spine 2012 16:163-71.


16. Gandhoke G, Wu JC, Rowland NC, et al. Anterior corpectomy versus posterior laminoplasty: is the risk of postoperative C-5 palsy different? Neurosurg Focus 2011 31:E12.

17. Wu JC, Ko CC, Yen YS, et al. Epidemiology of cervical spondylotic myelopathy and its risk of causing spinal cord injury: a national cohort study. Neurosurg Focus 2013 35:E10.

18. Matz PG, Anderson PA, Holly LT, et al. The natural history of cervical spondylotic myelopathy. J Neurosurg Spine 2009 11:104-11.


19. Resnick DK, Anderson PA, Kaiser MG, et al. Electrophysiological monitoring during surgery for cervical degenerative myelopathy and radiculopathy. J Neurosurg Spine 2009 11:245-52.


20. Matz PG, Holly LT, Mummaneni PV, et al. Anterior cervical surgery for the treatment of cervical degenerative myelopathy. J Neurosurg Spine 2009 11:170-3.


21. Matz PG, Anderson PA, Groff MW, et al. Cervical laminoplasty for the treatment of cervical degenerative myelopathy. J Neurosurg Spine 2009 11:157-69.


22. Anderson PA, Matz PG, Groff MW, et al. Laminectomy and fusion for the treatment of cervical degenerative myelopathy. J Neurosurg Spine 2009 11:150-6.


23. Ryken TC, Heary RF, Matz PG, et al. Cervical laminectomy for the treatment of cervical degenerative myelopathy. J Neurosurg Spine 2009 11:142-9.


24. Mummaneni PV, Kaiser MG, Matz PG, et al. Cervical surgical techniques for the treatment of cervical spondylotic myelopathy. J Neurosurg Spine 2009 11:130-41.


25. Holly LT, Matz PG, Anderson PA, et al. Clinical prognostic indicators of surgical outcome in cervical spondylotic myelopathy. J Neurosurg Spine 2009 11:112-8.


26. Northover JR, Wild JB, Braybrooke J, et al. The epidemiology of cervical spondylotic myelopathy. Skeletal Radiol 2012 41:1543-6.


27. Mizuno J, Nakagawa H. Outcome analysis of anterior decompressive surgery and fusion for cervical ossification of the posterior longitudinal ligament: report of 107 cases and review of the literature. Neurosurg Focus 2001 10:E6.

28. Ozer AF, Oktenoglu T, Cosar M, et al. Long-term follow-up after open-window corpectomy in patients with advanced cervical spondylosis and/or ossification of the posterior longitudinal ligament. J Spinal Disord Tech 2009 22:14-20.


29. Belanger TA, Roh JS, Hanks SE, et al. Ossification of the posterior longitudinal ligament. Results of anterior cervical decompression and arthrodesis in sixty-one North American patients. J Bone Joint Surg Am 2005 87:610-5.


30. Chen Y, Guo Y, Lu X, et al. Surgical strategy for multilevel severe ossification of posterior longitudinal ligament in the cervical spine. J Spinal Disord Tech 2011 24:24-30.


31. Dalbayrak S, Yilmaz M, Naderi S. "Skip" corpectomy in the treatment of multilevel cervical spondylotic myelopathy and ossified posterior longitudinal ligament. J Neurosurg Spine 2010 12:33-8.


32. Sakou T, Matsunaga S, Koga H. Recent progress in the study of pathogenesis of ossification of the posterior longitudinal ligament. J Orthop Sci 2000 5:310-5.


33. Schmidt MH, Quinones-Hinojosa A, Rosenberg WS. Cervical myelopathy associated with degenerative spine disease and ossification of the posterior longitudinal ligament. Semin Neurol 2002 22:143-8.


34. Murakami M, Seichi A, Chikuda H, et al. Long-term follow-up of the progression of ossification of the posterior longitudinal ligament. J Neurosurg Spine 2010 12:577-9.


35. Matsunaga S, Sakou T, Taketomi E, et al. Clinical course of patients with ossification of the posterior longitudinal ligament: a minimum 10-year cohort study. J Neurosurg 2004 100(3 Suppl Spine):245-8.


36. Matsunaga S, Kukita M, Hayashi K, et al. Pathogenesis of myelopathy in patients with ossification of the posterior longitudinal ligament. J Neurosurg 2002 96(2 Suppl):168-72.


37. Mochizuki M, Aiba A, Hashimoto M, et al. Cervical myelopathy in patients with ossification of the posterior longitudinal ligament. J Neurosurg Spine 2009 10:122-8.


38. Koyanagi I, Iwasaki Y, Hida K, et al. Acute cervical cord injury associated with ossification of the posterior longitudinal ligament. Neurosurgery 2003 53:887-91.


39. Sugimoto Y, Ito Y, Tanaka M, et al. Cervical cord injury in patients with ankylosed spines: progressive paraplegia in two patients after posterior fusion without decompression. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 2009 34:E861-3.


40. Endo S, Shimamura T, Nakae H, et al. Cervical spinal cord injury associated with ossification of the posterior longitudinal ligament. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 1994 113:218-21.


41. Ogawa Y, Toyama Y, Chiba K, et al. Long-term results of expansive open-door laminoplasty for ossification of the posterior longitudinal ligament of the cervical spine. J Neurosurg Spine 2004 1:168-74.


42. Rajshekhar V, Kumar GS. Functional outcome after central corpectomy in poor-grade patients with cervical spondylotic myelopathy or ossified posterior longitudinal ligament. Neurosurgery 2005 56:1279-84.


43. Wei-bing X, Wun-Jer S, Gang L, et al. Reconstructive techniques study after anterior decompression of multilevel cervical spondylotic myelopathy. J Spinal Disord Tech 2009 22:511-5.


44. Wang X, Chen Y, Chen D, et al. Removal of posterior longitudinal ligament in anterior decompression for cervical spondylotic myelopathy. J Spinal Disord Tech 2009 22:404-7.


45. Uchida K, Nakajima H, Sato R, et al. Cervical spondylotic myelopathy associated with kyphosis or sagittal sigmoid alignment: outcome after anterior or posterior decompression. J Neurosurg Spine 2009 11:521-8.


46. Matsumoto M, Nojiri K, Chiba K, et al. Open-door laminoplasty for cervical myelopathy resulting from adjacent-segment disease in patients with previous anterior cervical decompression and fusion. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 2006 31:1332-7.


47. Masaki Y, Yamazaki M, Okawa A, et al. An analysis of factors causing poor surgical outcome in patients with cervical myelopathy due to ossification of the posterior longitudinal ligament: anterior decompression with spinal fusion versus laminoplasty. J Spinal Disord Tech 2007 20:7-13.


48. Mayr MT, Subach BR, Comey CH, et al. Cervical spinal stenosis: outcome after anterior corpectomy, allograft reconstruction, and instrumentation. J Neurosurg 2002 96(1 Suppl):10-6.


49. Highsmith JM, Dhall SS, Haid RW Jr, et al. Treatment of cervical stenotic myelopathy: a cost and outcome comparison of laminoplasty versus laminectomy and lateral mass fusion. J Neurosurg Spine 2011 14:619-25.


50. Cabraja M, Abbushi A, Koeppen D, et al. Comparison between anterior and posterior decompression with instrumentation for cervical spondylotic myelopathy: sagittal alignment and clinical outcome. Neurosurg Focus 2010 28:E15.

51. Emery SE, Bohlman HH, Bolesta MJ, et al. Anterior cervical decompression and arthrodesis for the treatment of cervical spondylotic myelopathy. Two to seventeen-year follow-up. J Bone Joint Surg Am 1998 80:941-51.


52. Farey ID, McAfee PC, Davis RF, et al. Pseudarthrosis of the cervical spine after anterior arthrodesis. Treatment by posterior nerve-root decompression, stabilization, and arthrodesis. J Bone Joint Surg Am 1990 72:1171-7.


53. Jho HD. Spinal cord decompression via microsurgical anterior foraminotomy for spondylotic cervical myelopathy. Minim Invasive Neurosurg 1997 40:124-9.


54. Jho HD. Decompression via microsurgical anterior foraminotomy for cervical spondylotic myelopathy. Technical note. J Neurosurg 1997 86:297-302.


55. Koakutsu T, Morozumi N, Ishii Y, et al. Anterior decompression and fusion versus laminoplasty for cervical myelopathy caused by soft disc herniation: a prospective multicenter study. J Orthop Sci 2010 15:71-8.


56. Lian XF, Xu JG, Zeng BF, et al. Noncontiguous anterior decompression and fusion for multilevel cervical spondylotic myelopathy: a prospective randomized control clinical study. Eur Spine J 2010 19:713-9.



57. Unnanuntana A. Anterior decompression and fusion for cervical spondylotic myelopathy. J Med Assoc Thai 1998 81:272-7.

58. Hasegawa K, Homma T, Chiba Y. Upper extremity palsy following cervical decompression surgery results from a transient spinal cord lesion. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 2007 32:E197-202.


59. Hashimoto M, Mochizuki M, Aiba A, et al. C5 palsy following anterior decompression and spinal fusion for cervical degenerative diseases. Eur Spine J 2010 19:1702-10.



60. Kaneko K, Hashiguchi A, Kato Y, et al. Investigation of motor dominant C5 paralysis after laminoplasty from the results of evoked spinal cord responses. J Spinal Disord Tech 2006 19:358-61.


61. Minoda Y, Nakamura H, Konishi S, et al. Palsy of the C5 nerve root after midsagittal-splitting laminoplasty of the cervical spine. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 2003 28:1123-7.


62. Takemitsu M, Cheung KM, Wong YW, et al. C5 nerve root palsy after cervical laminoplasty and posterior fusion with instrumentation. J Spinal Disord Tech 2008 21:267-72.


63. Tanaka N, Nakanishi K, Fujiwara Y, et al. Postoperative segmental C5 palsy after cervical laminoplasty may occur without intraoperative nerve injury: a prospective study with transcranial electric motor-evoked potentials. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 2006 31:3013-7.






























